vue组件化实践
组件化
vue组件系统提供了一种抽象,让我们可以使用独立可复用的组件来构建大型应用,任意类型的应用界 面都可以抽象为一个组件树。组件化能提高开发效率,方便重复使用,简化调试步骤,提升项目可维护 性,便于多人协同开发。
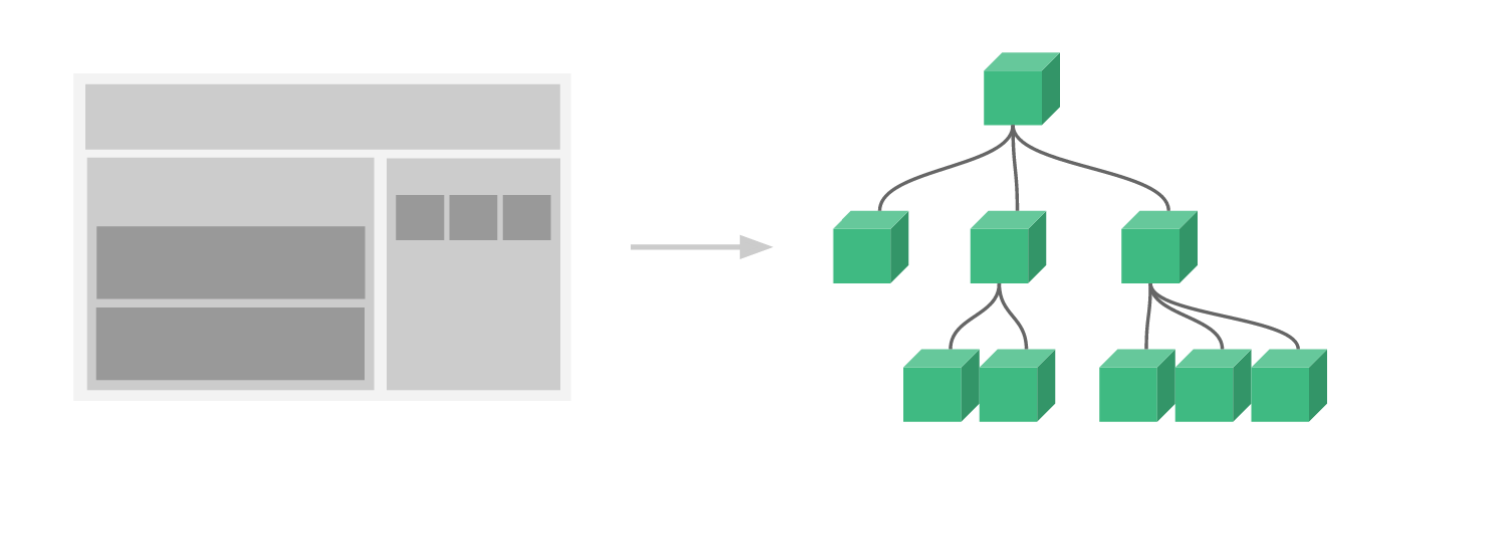
组件通信常用方式
1. props
父给子传值
// child
props: { msg: String }
// parent
<HelloWorld msg="Welcome to Your Vue.js App"/>
2. 自定义事件
子给父传值
// child this.$emit('add', good)
// parent
<Cart @add="cartAdd($event)"></Cart>
3. 事件总线
任意两个组件之间传值常用事件总线 或 vuex的方式。
// Bus:事件派发、监听和回调管理 class Bus {
constructor(){ this.callbacks = {}
}
$on(name, fn){
this.callbacks[name] = this.callbacks[name] || []
this.callbacks[name].push(fn) }
$emit(name, args){ if(this.callbacks[name]){
this.callbacks[name].forEach(cb => cb(args)) }
} }
// main.js
Vue.prototype.$bus = new Bus()
// child1
this.$bus.$on('foo', handle) // child2 this.$bus.$emit('foo')
实践中通常用Vue代替Bus,因为Vue已经实现了相应接口
4. vuex
创建唯一的全局数据管理者store,通过它管理数据并通知组件状态变更。
5. $parent/$root
兄弟组件之间通信可通过共同祖辈搭桥,
$parent或$root。
// brother1
this.$parent.$on('foo', handle)
// brother2
this.$parent.$emit('foo')
6. $children
父组件可以通过
$children访问子组件实现父子通信。
// parent
this.$children[0].xx = 'xxx'
7. $attrs/$listeners
包含了父作用域中不作为 prop 被识别 (且获取) 的特性绑定 ( class 和 style 除外)。当一个组件没有 声明任何 prop 时,这里会包含所有父作用域的绑定 ( class 和 style 除外),并且可以通过
v- bind="$attrs"传入内部组件——在创建高级别的组件时非常有用。
// child:并未在props中声明foo
<p>{{$attrs.foo}}</p>
// parent
<HelloWorld foo="foo"/>
8. refs
获取子节点引用
// parent
<HelloWorld ref="hw"/>
mounted() {
this.$refs.hw.xx = 'xxx'
}
9. provide/inject
能够实现祖先和后代之间传值
// ancestor
provide() {
return {foo: 'foo'}
}
// descendant
inject: ['foo']
实例
// index.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>组件通信</h2>
<!-- props, 自定义事件 -->
<Child1 msg="some msg from parent" @some-event="onSomeEvent"></Child1>
<!-- 事件总线 -->
<Child2 msg="other msg"></Child2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Child1 from '@/components/communication/Child1.vue'
import Child2 from '@/components/communication/Child2.vue'
export default {
components: {
Child1, Child2,
// Child3: () => import('./Child3.vue')
},
methods: {
onSomeEvent(msg) {
console.log('Communition:', msg);
}
},
mounted () {
// $children持有所有自定义组件
// 它不保证顺序
console.log(this.$children);
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
// child1.vue
<template>
<div @click="$emit('some-event', 'msg from child1')">
<h3>child1</h3>
<p>{{msg}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
msg: {
type: String,
default: ''
},
},
mounted () {
// this.$bus.$on('event-from-child2', msg => {
// console.log('Child1:', msg);
// });
this.$parent.$on('event-from-child2', msg => {
console.log('Child1:', msg);
});
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
// child2.vue
<template>
<div>
<!-- 展开$attrs对象 -->
<h3 v-bind="$attrs">child2</h3>
<button @click="sendToChild1">给child1发送消息</button>
<!-- $attrs -->
<p>{{$attrs.msg}}</p>
<!-- inject -->
<p>{{foo}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
inheritAttrs: false,
inject: ['foo'],
methods: {
sendToChild1() {
// 利用事件总线发送事件
// this.$bus.$emit('event-from-child2', 'some msg from child2')
this.$parent.$emit('event-from-child2', 'some msg from child2')
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
插槽
插槽语法是Vue 实现的内容分发 API,用于复合组件开发。该技术在通用组件库开发中有大量应用
1. 匿名插槽
// comp1
<div>
<slot></slot>
</div>
// parent
<comp>hello</comp>
2. 具名插槽
将内容分发到子组件指定位置
// comp2
<div>
<slot></slot>
<slot name="content"></slot>
</div>
// parent
<Comp2>
<!-- 默认插槽用default做参数 -->
<template v-slot:default>具名插槽</template> <!-- 具名插槽用插槽名做参数 -->
<template v-slot:content>内容...</template>
</Comp2>
3. 作用域插槽
分发内容要用到子组件中的数据
// comp3
<div>
<slot :foo="foo"></slot>
</div>
// parent
<Comp3>
<!-- 把v-slot的值指定为作用域上下文对象 --> <template v-slot:default="slotProps"> 来自子组件数据:{{slotProps.foo}} </template>
</Comp3>
范例
// 子组件 Layout.vue
<template>
<div>
<div class="header">
<slot name="header"></slot>
</div>
<div class="body">
<slot></slot>
</div>
<div class="footer">
<slot name="footer" :fc="footerContent"></slot>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
remark: [
'好好学习,天天向上',
'学习永远不晚',
'学习知识要善于思考,思考,再思考',
'学习的敌人是自己的满足,要认真学习一点东西,必须从不自满开始',
'构成我们学习最大障碍的是已知的东西,而不是未知的东西',
'在今天和明天之间,有一段很长的时间;趁你还有精神的时候,学习迅速办事',
'三人行必有我师焉;择其善者而从之,其不善者而改之'
]
}
},
computed: {
footerContent() {
return this.remark[new Date().getDay() - 1]
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.header {
background-color: rgb(252, 175, 175);
}
.body {
display: flex;
background-color: rgb(144, 250, 134);
min-height: 100px;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.footer {
background-color: rgb(114, 116, 255);
}
</style>
//父组件 index.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>插槽</h2>
<!-- 插槽 -->
<Layout>
<!-- 具名插槽 -->
<template v-slot:header>全栈工程师</template>
<!-- 匿名插槽 -->
<template>content...</template>
<!-- 作用域插槽 -->
<template v-slot:footer="{fc}">{{fc}}</template>
</Layout>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Layout from '@/components/slots/Layout.vue'
export default {
components: {
Layout
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
组件化实战
通用表单组件
收集数据、校验数据并提交。
实现KForm 指定数据、校验规则
KformItem
- label标签添加
- 执行校验
- 显示错误信息
KInput
- 维护数据
<template>
<el-form :model="userInfo" :rules="rules" ref="loginForm">
<el-form-item label="用户名" prop="name">
<el-input v-model="userInfo.name"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item label="密码" prop="password">
<el-input v-model="userInfo.password" type="password"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item>
<el-button @click="login">登录</el-button>
</el-form-item>
</el-form>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
userInfo: {
username: "",
password: ""
},
rules: {
username: [{ required: true, message: "请输入用户名称" }],
password: [{ required: true, message: "请输入密码" }]
}
};
},
methods: {
login() {
this.$refs["loginForm"].validate(valid => {
if (valid) {
alert("submit");
} else {
console.log("error submit!");
return false;
}
});
}
}
};
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
**1. **KInput
// 创建components/form/KInput.vue
<template>
<div>
<!-- 管理数据:实现双绑 -->
<!-- :value, @input -->
<input :type="type" :value="value" @input="onInput"
v-bind="$attrs">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
inheritAttrs: false , // 关闭特性继承
props: {
value: {
type: String,
default: ''
},
type: {
type: String,
default: 'text'
}
},
methods: {
onInput(e) {
this.$emit('input', e.target.value)
// 值发生变化的时候就是需要校验的时候
this.$parent.$emit('validate')
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
- 使用KInput
创建components/form/index.vue,添加如下代码:
<template>
<div>
<h3>KForm表单</h3>
<hr>
<k-input v-model="model.username"></k-input>
<k-input type="password" v-model="model.password"></k-input>
</div>
</template>
export default {
components: {
KInput
},
data() {
return {
model: { username: "tom", password: "" },
};
}
};
</script>
- 实现KFormItem
创建components/form/KFormItem.vue
<template>
<div>
<!-- label标签 -->
<label v-if="label">{{label}}</label>
<!-- 容器,放插槽 -->
<slot></slot>
<!-- 错误信息展示 -->
<p v-if="error" class="error">{{error}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Schema from 'async-validator'
export default {
inject: ['form'],
data() {
return {
error: ''
}
},
props: {
label: {
type: String,
default: ''
},
prop: {
type: String,
default: ''
}
},
mounted () {
// 监听校验事件
this.$on('validate', () => {
this.validate()
})
},
methods: {
validate() {
// 执行校验
// 1.获取值和校验规则
const rules = this.form.rules[this.prop]
const value = this.form.model[this.prop]
// 2.执行校验:使用官方也使用的async-validator
// 创建描述对象
const descriptor = {[this.prop]:rules}
// 创建校验器
const validator = new Schema(descriptor)
// 执行校验
return validator.validate({[this.prop]:value}, errors => {
// 如果errors存在,则说明校验失败
if (errors) {
this.error = errors[0].message
} else {
this.error = ''
}
})
}
},
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.error{
color: red
}
</style>
- 使用KFormItem
components/form/index.vue,添加基础代码:
<template>
<div>
<h3>KForm表单</h3>
<hr>
<k-form-item label="用户名" prop="username">
<k-input v-model="model.username"></k-input> </k-form-item>
<k-form-item label="确认密码" prop="password">
<k-input type="password" v-model="model.password"></k-input>
</k-form-item> </div>
</template>
- 实现KForm
<template>
<div>
<!-- 容器:存放所有表单项 -->
<!-- 存储值载体:保存大家数据和校验规则 -->
<slot></slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 我们平时写的组件是一个组件配置对象
export default {
provide() {
return {
// 直接把当前组件实例传递下去
// 传递下去的对象是响应式的则还可以响应式
form: this
};
},
props: {
// 数据模型
model: {
type: Object,
required: true
},
rules: Object
},
methods: {
validate(cb) {
// 遍历肚子里面的所有FormItem,执行他们的validate方法
// 全部通过才算通过
// tasks是校验结果的Promise组成的数组
const tasks = this.$children
.filter(item => item.prop)
.map(item => item.validate());
// 统一判断
Promise.all(tasks)
.then(() => cb(true))
.catch(() => cb(false));
}
}
};
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
- 使用KForm
components/form/index.vue,添加基础代码:
< template > <div > <h3 > KForm表单 < /h3>
<hr>
<k-form :model="model" :rules="rules" ref="loginForm">
...
</k - form > </div>
</template > <script > import KForm from "./KForm";
export default {
components:
{
KForm,
},
data() {
return {
rules: {
username: [{
required: true,
message: "请输入用户名"
}],
password: [{
required: true,
message: "请输入密码"
}]
}
};
},
methods: {
submitForm() {
this.$refs['loginForm'].validate(valid = >{
if (valid) {
alert("请求登录!");
} else {
alert("校验失败!");
}
});
}
}
}; < /script>/
- 数据校验
Input通知校验
onInput(e) { // ...
// $parent指FormItem
this.$parent.$emit('validate');
}
FormItem监听校验通知,获取规则并执行校验
inject: ['form'],
// 注入 mounted(){// 监听校验事件
this.$on('validate', () = >{
this.validate()
})
},
methods: {
validate() {
// 获取对应FormItem校验规则 console.log(this.form.rules[this.prop]);
}
},
import Schema from "async-validator";
validate() {
// 获取对应FormItem校验规则
const rules = this.form.rules[this.prop];
// 获取校验值
const value = this.form.model[this.prop];
// 校验
const schema = new Schema(descriptor);
// 返回Promise,没有触发catch就说明验证通过
return schema.validate({ [this.prop] : value
},
errors = >{
if (errors) {
// 将错误信息显示
this.error = errors[0].message;
} else {
// 校验通过 this.error = "";
}
});
}
表单全局验证,为Form提供validate方法
validate(cb) {
// 调用所有含有prop属性的子组件的validate方法并得到Promise数组 const tasks = this.$children
.filter(item = >item.prop).map(item = >item.validate());
// 所有任务必须全部成功才算校验通过,任一失败则校验失败
Promise.all(tasks).then(() = >cb(true)).catch(() = >cb(false))
}
实现弹窗组件
弹窗这类组件的特点是它们在当前vue 实例之外独立存在,通常挂载于body;它们是通过JS动态创建的,不需要在任何组件中声明。常⻅使用姿势
this.$create(Notice, {
title: '喊你来搬砖',
message: '提示信息',
duration: 1000
}).show();
create函数
import Vue from "vue";
// 创建函数接收要创建组件定义
function create(Component, props) {
// 创建一个Vue新实例 const vm = new Vue({
render(h) {
// render函数将传入组件配置对象转换为虚拟dom console.log(h(Component, { props })); return h(Component, { props });
}
}).$mount(); //执行挂载函数,但未指定挂载目标,表示只执行初始化工作
// 将生成dom元素追加至
body document.body.appendChild(vm.$el);
// 给组件实例添加销毁方法
const comp = vm.$children[0];
comp.remove = () = >{
document.body.removeChild(vm.$el);
vm.$destroy();
};
return comp;
}
// 暴露调用接口
export default create
另一种创建组件实例的方式:
Vue.extend(Component)
通知组件
建通知组件,Notice.vue
<template>
<div class="box" v-if="isShow">
<h3>{{title}}</h3>
<p class="box-content">{{message}}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: {
title: {
type: String,
default: ""
},
message: {
type: String,
default: ""
},
duration: {
type: Number,
default: 2000
}
},
data() {
return {
isShow: false
};
},
methods: {
show() {
this.isShow = true;
setTimeout(this.hide, this.duration);
},
hide() {
this.isShow = false;
this.remove();
}
}
};
</script>
<style>
.box {
position: fixed;
width: 100%;
top: 16px;
left: 0;
text-align: center;
pointer-events: none;
background-color: #fff;
border: grey 3px solid;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.box-content {
width: 200px;
margin: 10px auto;
font-size: 14px;
padding: 8px 16px;
background: #fff;
border-radius: 3px;
margin-bottom: 8px;
}
</style>
阅读全文
